|
Hi, I'm Gaurav. I am a PhD student at University of Maryland, Baltimore County advised by Prof. Nirmalya Roy. My research focuses on multi-agent systems, with a particular emphasis on addressing challenges in contested environments. Previously, I worked as a Research Assistant at MiCoSys Lab with Prof. Saptarshi Sengupta, where I developed deep learning techniques for predicting the remaining useful life of lithium-ion batteries. LinkedIn / Google Scholar / GitHub / CV Currently seeking a summer internship to apply my expertise in multi-agent systems, computer vision, & machine learning to solve real-world problems. |

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Recent News
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|

|
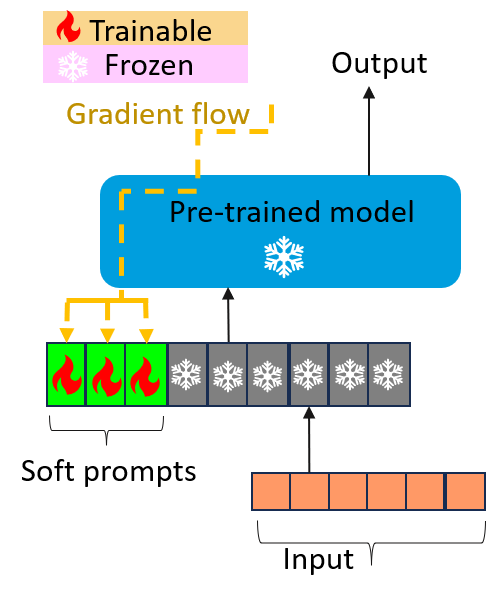
Gaurav Shinde, Anuradha Ravi, Emon Dey, Shadman Sakib, Milind Rampure, Nirmalya Roy WIREs DMKD, 2025 paper Vision-language models (VLMs) integrate visual and textual information, enabling a wide range of applications such as image captioning and visual question answering, making them crucial for modern AI systems. However, their high computational demands pose challenges for real-time applications. This has led to a growing focus on developing efficient vision language models. In this survey, we review key techniques for optimizing VLMs on edge and resource-constrained devices. We also explore compact VLM architectures, frameworks and provide detailed insightsinto the performance-memory tradeoffs of efficient VLMs. |


|
Shadman Sakib, Gaurav Shinde, Emon Dey, Nirmalya Roy IEEE SmartComp, 2025 paper Continuous, non-invasive respiratory rate (RR) monitoring is essential for the early diagnosis of many medical problems. However, conventional contact-based sensors frequently under-perform in dynamic situations that can be uncomfortable and require human intervention. To overcome these limitations, we propose E2RespUNet, an end-to-end system that uses multimodal video data to estimate breathing rates and reconstruct respiratory signals using an attention-enhanced U-Net architecture. Our method combines optical flow analysis with preprocessing, detrending, and normalization to reliably extract chest motion features in a variety of settings. According to our study in both the temporal and frequency domains, E2RespUNet surpasses existing baseline models by lowering the mean absolute error by up to 21 % in the sleep dataset and by up to 28% in the in-house dataset. |

|
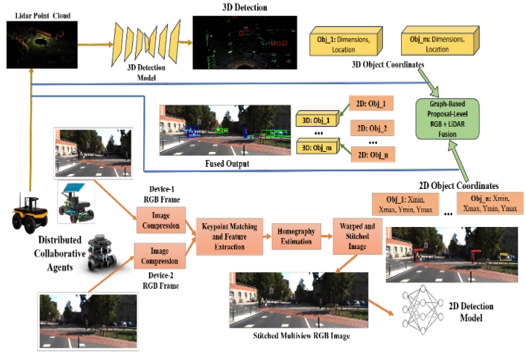
MS Anwar, Anuradha Ravi, Emon Dey, Gaurav Shinde, Indrajeet Ghosh, Jade Freeman, Carl Busart, Andre Harrison, Nirmalya Roy IEEE DECOSS-IoT, 2025 paper Integrating multimodal data such as RGB and LiDAR from multiple views significantly increases computational and communication demands, which can be challenging for resource-constrained autonomous agents while meeting the time-critical deadlines required for various mission-critical applications. To address this challenge, we propose CoOpTex, a collaborative task execution framework designed for cooperative perception in distributed autonomous systems (DAS). |

|
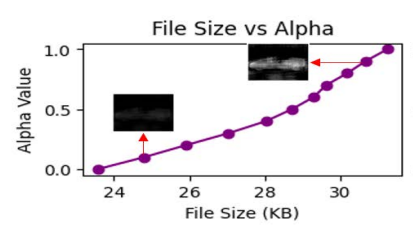
Gaurav Shinde, Anuradha Ravi, Emon Dey, Jared Lewis, Nirmalya Roy IEEE PerCom Worshop, 2025 paper In network-constrained environments, distributed multi-agent systems—such as UGVs and UAVs—must communicate effectively to support computationally demanding scene perception tasks like semantic and instance segmentation. These tasks are challenging because they require high accuracy even when using low-quality images, and the network limitations restrict the amount of data that can be transmitted between agents. To overcome the above challenges, we propose TAVIC-DAS to perform a task and channel-aware variable-rate image compression to enable distributed task execution and minimize communication latency by transmitting compressed images. TAVIC-DAS proposes a novel image compression and decompression framework (distributed across agents) that integrates channel parameters such as RSSI and data rate into a task-specific "semantic segmentation" DNN to generate masks representing the object of interest in the scene (ROI maps) by determining a high pixel density needed to represent objects of interest and low density to represents surrounding pixels within an image |

|
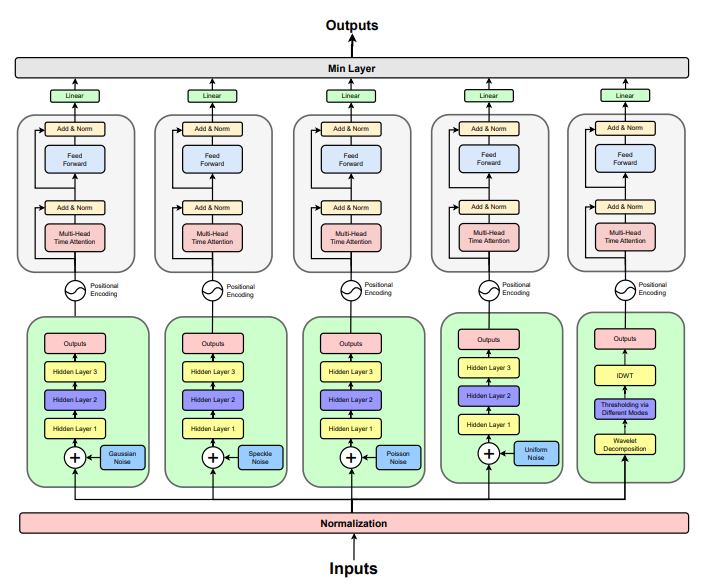
Gaurav Shinde, Rohan Mohapatra, Pooja Krishan, Saptarshi Sengupta IEEE BigData, 2023 paper The usage of Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries has gained widespread popularity across various industries, from powering portable electronic devices to propelling electric vehicles and supporting energy storage systems. A central challenge in Li-ion battery reliability lies in accurately predicting their Remaining Useful Life (RUL), which is a critical measure for proactive maintenance and predictive analytics. This study presents a novel approach that harnesses the power of multiple denoising modules, each trained to address specific types of noise commonly encountered in battery data. Specifically, a denoising auto-encoder and a wavelet denoiser are used to generate encoded/decomposed representations, which are subsequently processed through dedicated self-attention transformer encoders. After extensive experimentation on NASA and CALCE data, a broad spectrum of health indicator values are estimated under a set of diverse noise patterns. The reported error metrics on these data are on par with or better than the state-of-the-art reported in recent literature. |
Website adapted from Jon Barron